코틀린 기반으로 스프링 프레임워크를 사용하는 경우 다양한 플러그인의 도움으로 보다 쉽게 개발을 진행할 수 있습니다. 어떤 플러그인이 있고 그것이 어떤 역할을 하는지에 대해서 정리해 보았습니다.
Kotlin Plugin 1 2 3 4 plugins { kotlin("plugin.spring" ) version "1.4.32" kotlin("plugin.jpa" ) version "1.4.32" }
코틀린 언어로 스프링을 사용하는 경우는 plugin.spring 플러그인은 필수적이고, JPA를 사용한다면 plugin.jpa 또 한 필수적으로 사용하게 됩니다. 각각의 플러그인에 대해서 이야기해보겠습니다.
plugin.spring 플러그인 all-open 해당 플러그인을 사용하면 아래 어노테이션이 있으면 all-open을 자동으로 추가시킵니다. 참고로 kotlin-allopen, plugin.spring는 동일한 프로젝트입니다.
@Component@Async@Transactional@Cacheable@SpringBootTest@Configuration, @Controller, @RestController, @Service, @Repository, @Component
1 2 3 class Foo { fun test () }
코틀린에서는 기본적으로 클래스에는 final 키워드가 추가되며, 위 코드도 final 키워드를 생략하더라도 자동으로 추가합니다.
1 2 3 public final class Foo public constructor () { public final fun test () Unit { } }
Foo 클래스를 빌드 하면 위처럼 final 키워드가 붙어 있는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
1 2 3 4 @Transactional class Foo { fun test () }
@Transactional 어노테이션을 붙이고 다시 빌드 해보고 클래스 파일을 살펴보겠습니다.
1 2 3 @org .springframework.transaction.annotation .Transactional public open class Foo public constructor () { public open fun test () Unit { } }
class, fun 키워드 앞에 open 키워드가 추가된 것을 확인할 수 있습니다. plugin.spring이 위의 어노테이션이 추가된 클래스에는 자동으로 open 키워드를 자동으로 추가합니다. Spring Initializr 를 이용해서 프로젝트를 구성하면 plugin.spring 플러그인은 자동 적용됩니다.
1 2 3 4 allOpen { annotation("javax.persistence.Entity" ) ... }
gradle 설정으로 특정 어노테이션에 대해서 allOpen을 동작 시킬 수 있습니다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 @Entity @Table(name = "book" ) class Book ( @Column(name = "title" , nullable = false) var title: String, @Column(name = "writer" , nullable = false) var writer: String, ... ) : AuditingEntity() { }
위 객체를 빌드 해서 클래스 파일을 확인하면 아래와 같습니다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @javax .persistence.Entity @javax .persistence.Table public open class Book public constructor (title: kotlin.String, writer: kotlin.String, publisher: kotlin.String, price: java.math.BigDecimal) : com.spring.sample.AuditingEntity { @field:javax .persistence.Column public open var price: java.math.BigDecimal @field:javax .persistence.Column public open var publisher: kotlin.String @field:javax .persistence.Column public open var title: kotlin.String @field:javax .persistence.Column public open var writer: kotlin.String }
특정 어노테이션에 open 키워드를 편리하기 추가할 수 있습니다.
all-open은 왜 필요할까?
Spring Boot 2.x 버전부터는 CGLIB Proxy 방식으로 Bean을 관리하고 있습니다. CGLIB Proxy는 Target Class를 상속받아 생성하기 때문에 open으로 상속이 가능한 상태이어야 합니다. 그러기 때문에 all-open 플러그인이 필요합니다.
no-arg no-arg는 argument가 없는 기본 생성자를 의미합니다. 클래스는 기본 생성자가 기본적으로 생성되며 다른 생성자를 만들면 기본 생성자는 명시적으로 선언하지 않는 이상 사라지게 됩니다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Bar (val name: String) { } public final class Bar public constructor (name: kotlin.String) { public final val name: kotlin.String } public final class Bar public constructor (name: kotlin.String) { public constructor () { } public final val name: kotlin.String }
no-arg는 주로 plugin.jpa 플러그인과 같이 사용됩니다. kotlin-spring 플러그인과 마찬가지로 @Entity, @Embeddable, @MappedSuperclass 어노테이션에 자동으로 동작합니다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 @Entity @Table(name = "book" ) class Book ( @Column(name = "title" , nullable = false) var title: String, @Column(name = "writer" , nullable = false) var writer: String, @Column(name = "publisher" , nullable = false) var publisher: String, @Column(name = "price" , nullable = false) var price: BigDecimal ) : AuditingEntity() { } public class Book extends AuditingEntity { ... public Book(@NotNull String title, @NotNull String writer, @NotNull String publisher, @NotNull BigDecimal price) { Intrinsics.checkNotNullParameter(title, "title" ); Intrinsics.checkNotNullParameter(writer, "writer" ); Intrinsics.checkNotNullParameter(publisher, "publisher" ); Intrinsics.checkNotNullParameter(price, "price" ); super (); this .title = title; this .writer = writer; this .publisher = publisher; this .price = price; } public Book() { } }
Book 객체에 기본 생성자가 없지만 plugin.jpa 플러그인으로 인해서 기본 생성자가 생성됩니다.
plugin.jpa 플러그인 no-arg에서 언급했듯이 plugin.jpa 플러그인을 사용 하면 @Entity, @Embeddable, @MappedSuperclass 어노테이션을 사용해면 no-arg생성자(기본 생성자)가 자동으로 생성됩니다.
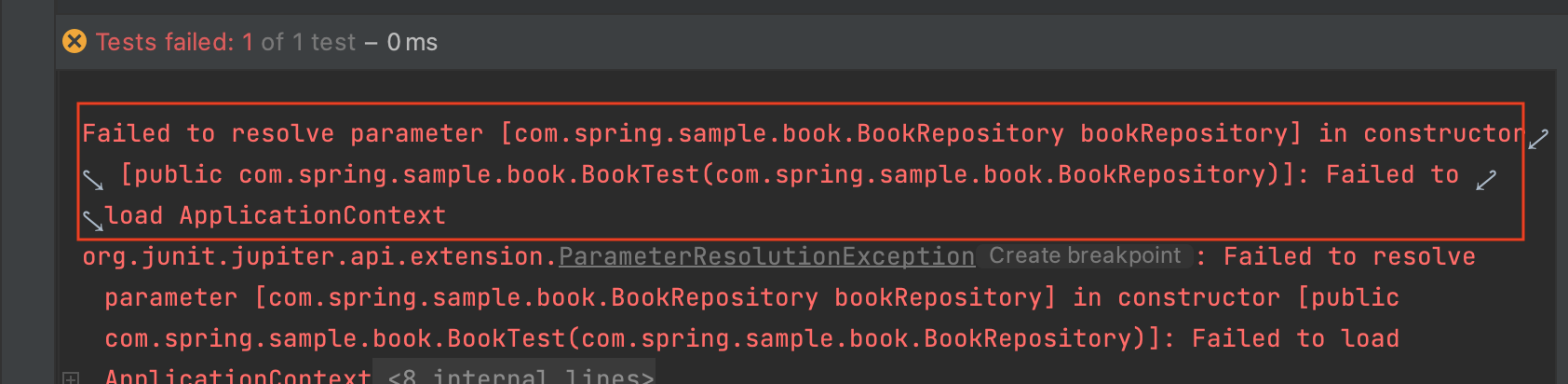
no-arg이 왜 필요할까? plugin.jpa 플러그인 없이, 즉 기본 생성자가 없는 상태에서 JPA 아래 테스트 코드를 실행해보겠습니다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 @Entity @Table(name = "book" ) class Book ( @Column(name = "title" , nullable = false) var title: String, @Column(name = "writer" , nullable = false) var writer: String, @Column(name = "publisher" , nullable = false) var publisher: String, @Column(name = "price" , nullable = false) var price: BigDecimal ) : AuditingEntity() @Transactional internal class BookTest ( private val bookRepository: BookRepository, ) : SpringTestSupport() { @Test internal fun `boot save`() bookRepository.save( Book( title = "title" , writer = "writer" , publisher = "publisher" , price = BigDecimal.TEN ) ) } }
기본 생성자가 없어 Error가 발생하는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다. Book 클래스 파일을 decompile 해서 코드를 확인해보겠습니다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public class Book extends AuditingEntity { ... public Book (@NotNull String title, @NotNull String writer, @NotNull String publisher, @NotNull BigDecimal price) { Intrinsics.checkNotNullParameter(title, "title" ); Intrinsics.checkNotNullParameter(writer, "writer" ); Intrinsics.checkNotNullParameter(publisher, "publisher" ); Intrinsics.checkNotNullParameter(price, "price" ); super (); this .title = title; this .writer = writer; this .publisher = publisher; this .price = price; } }
all-argument생성자는 존재하지만, no-arg생성자는 존재하지 않습니다. Hibernate는 Reflection으로 객체를 생성하기 때문에 protected 이상의 생성자가 필요합니다. 다시 plugin.jpa 플러그인 적용해서 decompile 해보겠습니다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class Book extends AuditingEntity { ... public Book (@NotNull String title, @NotNull String writer, @NotNull String publisher, @NotNull BigDecimal price) { Intrinsics.checkNotNullParameter(title, "title" ); Intrinsics.checkNotNullParameter(writer, "writer" ); Intrinsics.checkNotNullParameter(publisher, "publisher" ); Intrinsics.checkNotNullParameter(price, "price" ); super (); this .title = title; this .writer = writer; this .publisher = publisher; this .price = price; } public Book () { } }
no-arg생성자가 코드가 있는 것을 확인할 수 있고, 테스트 코드도 정상적으로 동작하는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
all-open In JPA 1 2 3 4 5 6 # build.gradle.kts allOpen { annotation("javax.persistence.Entity") annotation("javax.persistence.MappedSuperclass") annotation("javax.persistence.Embeddable") }
plugin.jpa을 사용하면 no-arg @Entity, @Embeddable, @MappedSuperclass 코드에 자동으로 추가되지만 all-open 명시적으로 위처럼 선언해야 합니다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 # allOpen 없는 경우� @javax .persistence.Entity @javax .persistence.Table public final class Book public constructor (title: kotlin.String, writer: kotlin.String, publisher: kotlin.String, price: java.math.BigDecimal) : com.spring.sample.AuditingEntity { @field:javax .persistence.Column public final var price: java.math.BigDecimal @field:javax .persistence.Column public final var publisher: kotlin.String @field:javax .persistence.Column public final var title: kotlin.String @field:javax .persistence.Column public final var writer: kotlin.String } # allOpen 있는 경우 @javax .persistence.Entity @javax .persistence.Table public open class Book public constructor (title: kotlin.String, writer: kotlin.String, publisher: kotlin.String, price: java.math.BigDecimal) : com.spring.sample.AuditingEntity { @field:javax .persistence.Column public open var price: java.math.BigDecimal @field:javax .persistence.Column public open var publisher: kotlin.String @field:javax .persistence.Column public open var title: kotlin.String @field:javax .persistence.Column public open var writer: kotlin.String }
위 코드의 차이점은 allOpen이 없는 경우 fianl 키워드가 있고, allOpen이 있는 경우 open 키워드가 있습니다. open 키워드가 없으면 Proxy 기반으로 Lazy 로딩을 할 수 없습니다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 @Entity @Table(name = "book" ) class Book ( @Column(name = "title" , nullable = false) var title: String, @ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY, targetEntity = Order::class) @JoinColumn(name = "order_id" , nullable = false) var order: Order ) : AuditingEntity() @Entity @Table(name = "orders" ) class Order ( @Column(name = "title" , nullable = false) var number: String ) : AuditingEntity()
@ManyToOne 관계이며, Lazy fetch 전략을 설정했습니다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @Test internal fun `lazy loading test`() val order = orderRepository.save(Order("202012-12" )) val book = bookRepository.save(Book(title = "title" , order = order)) entityManager.clear() val findBook = bookRepository.findByIdOrNull(book.id!!)!! }
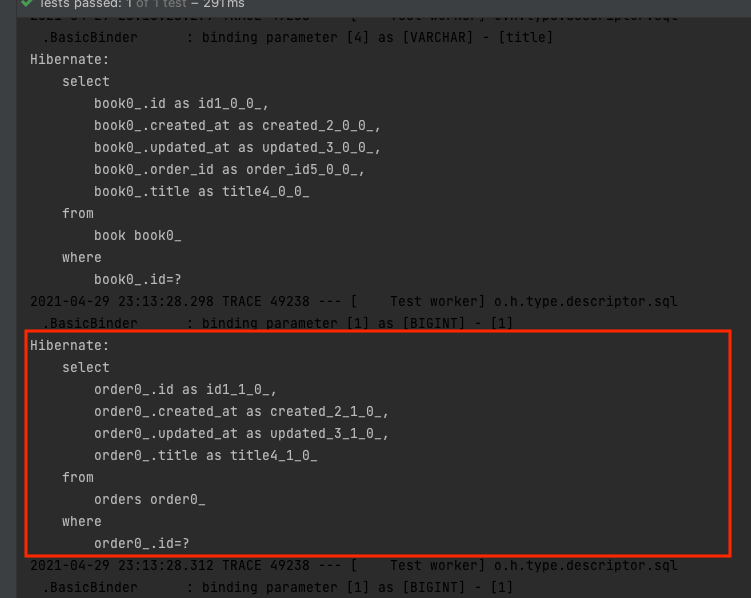
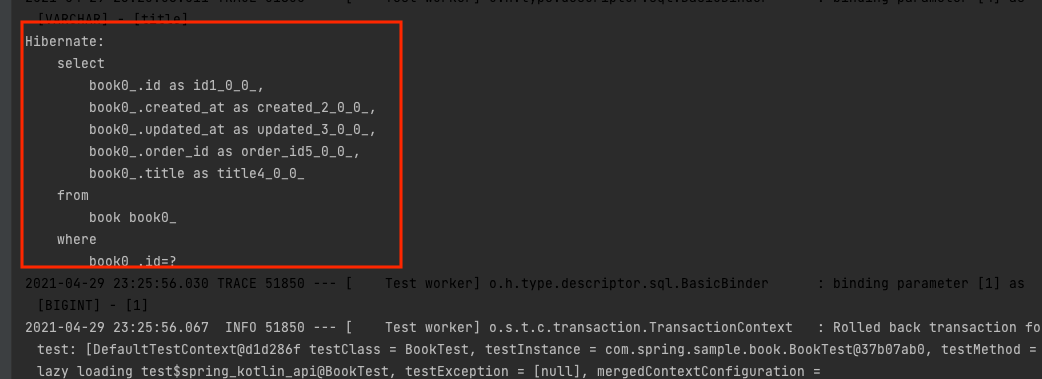
Lazy 패치 전략을 사용했기 때문에 book에 대한 조회 시 order에 대한 조회가 쿼리가 발생하지 않을 것이라고 예상했지만 결과는 다릅니다.
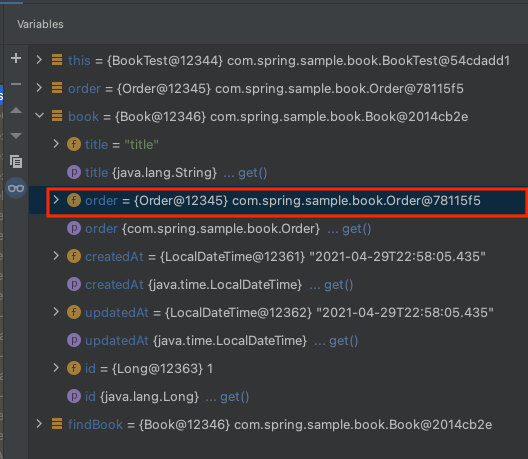
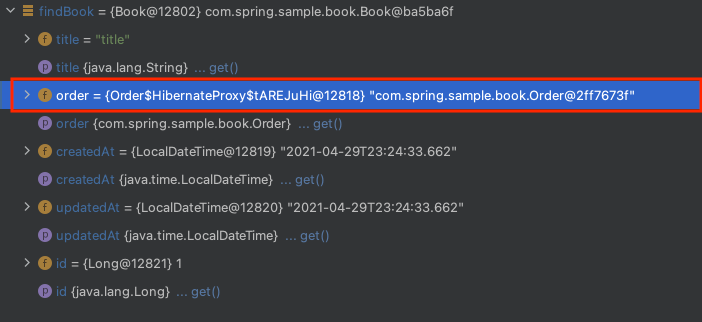
order에 대한 조회 발생합니다. 디버깅 모드를 활용해서 해당 값을 확인해보겠습니다.
Lazy Loading이기 때문에 order는 Proxy 객체이어야 합니다. 하지만 Proxy 객체가 아니라 실제 order 객체를 가지고 있는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다. 그 이유는 Kotlin은 기본적으로 final이기 때문에 Proxy 클래스를 생성하지 못합니다. Proxy 클래스를 생성하기 위해서는 상속이 가능해야 하므로 open이 필요한데 없으니 Proxy 기반으로 Lazy Loading을 진행할 수 없는 것입니다. 그렇다면 allOpen을 적용하고 다시 테스트해보겠습니다.
Lazy Loading이 정상적으로 동작하고 Proxy 기반으로 order 객체를 가져오는것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
jackson-module-kotlin 모듈 Spring Initializr 를 이용해서 Spring Web MVC 프로젝트를 생성하게 되면 com.fasterxml.jackson.module:jackson-module-kotlin 디펜던시가 자동으로 추가된다. jackson-module-kotlin 는 기존 Jackson으로 deserialize 하기 위해서는 기본 생성자가 반드시 필요합니다. 하지만 코틀린에서 data class의 객체를 deserialize를 진행하게 되면 기본 생성자가 없기 때문에 아래와 같은 예외가 발생합니다.
1 (no Creators, like default construct, exist): cannot deserialize from Object valu...
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 class SampleRequestBody { private String name; private int age; }
위 같은 자바 코드는 all arguments 생성자가 주석인 경우 기본 생성자를 명시적으로 선언하지 않아도 존재하기 때문에 deserialize 진행에 문제가 없습니다. 만약 다른 생성자가 있다면 명시적으로 기본 생성자를 작성하지 않으면 예외가 발생합니다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 data class SampleRequestBody ( val name: String, val age: Int ) public final class SampleRequestBody { @NotNull private final String name; private final int age; @NotNull public final String getName() { return this .name; } public final int getAge() { return this .age; } public SampleRequestBody(@NotNull String name, int age) { Intrinsics.checkNotNullParameter(name, "name" ); super (); this .name = name; this .age = age; } .. }
코틀린의 data class는 all argument 생성자만 생성하기 때문에 기존 jackson으로 deserialize를 못하고 jackson-module-kotlin을 통해서 단일 생성자로 deserialize를 진행할 수 있습니다. 하지만 최근에는 이 부분도 개선되어 굳이 jackson-module-kotlin 모듈의 도움 없이 기본 생성자가 없이도 deserialize를 진행할 수 있습니다.
ParameterName 이용
spring-boot-starter-web의 디펜던시를 통해서 jackson-module-parameter-names는 자동으로 추가됩니다. 즉 ParameterName 모듈은 이미 사용할 수 있는 상태입니다. ParameterNameModule 모듈에 대한 자세한 정리는 Jackson으로 파싱한 JSON 속성값을 생성자로 전달하기 에 잘 정리되어 있어 한 번 읽어 보시는 것을 권유 드립니다.
해당 블로그의 내용을 정리하면 다음과 같습니다.
@JsonProperty("ip") 방식(Jackson Deserialization Annotations: @JsonCreator 참고 ) 같은 방식으로 생성자 파라미터와, json 필드명이 일치한다면 따로 속성을 지정하지 않아도 가져올 수 있음JDK 8 이전까지는 Reflection만으로는 파라미터 이름을 가져올 수 없었으나 JDK 8 이상의 경우 컴파일 할 때 -parameters 옵션을 붙이면 Reflection API로 파라미터 정보를 가져올 수 있습니다.Spring Boot Gradle Plugin 플러그인에서 Java 컴파일의 -parameters 옵션을 자동으로 추가됩니다.
@RequestBody를 통해서 deserialize를 진행할 때 별다른 설정을 하지 않았다면 WebMvcAutoConfiguration 클래스의 정의된 아래의 코드에 의해 결정됩니다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class WebMvcAutoConfiguration { ... public void configureMessageConverters (List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) { this .messageConvertersProvider .ifAvailable((customConverters) -> converters.addAll(customConverters.getConverters())); } } public class JacksonAutoConfiguration { ... @Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) @ConditionalOnClass(ParameterNamesModule.class) static class ParameterNamesModuleConfiguration { @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean ParameterNamesModule parameterNamesModule () { return new ParameterNamesModule (JsonCreator.Mode.DEFAULT); } } }
HttpMessageConverter 리스트에 기본으로 추가되는 Jackson에는 ParameterNamesModule이 추가되어 있습니다. 만약 WebMvcConfigurer 인터페이스를 기반으로 extendMessageConverters를 재정의 해서 사용하는 경우에는 ParameterNamesModule 설정을 추가해야 합니다. 결과 적으로 jackson-module-kotlin 모듈 없이 jackson-module-parameter-names 모듈만으로 deserialize를 진행할 수 있습니다.
참고